Understanding DMARC Report Data
Report Dashboard Components
Message Volume
Total emails claiming to be from your domain, broken down by source and authentication status.
Authentication Results
SPF and DKIM pass/fail rates, alignment status, and overall DMARC compliance.
Source Analysis
Breakdown of sending sources, including legitimate services and potential threats.
Reading Report Tables
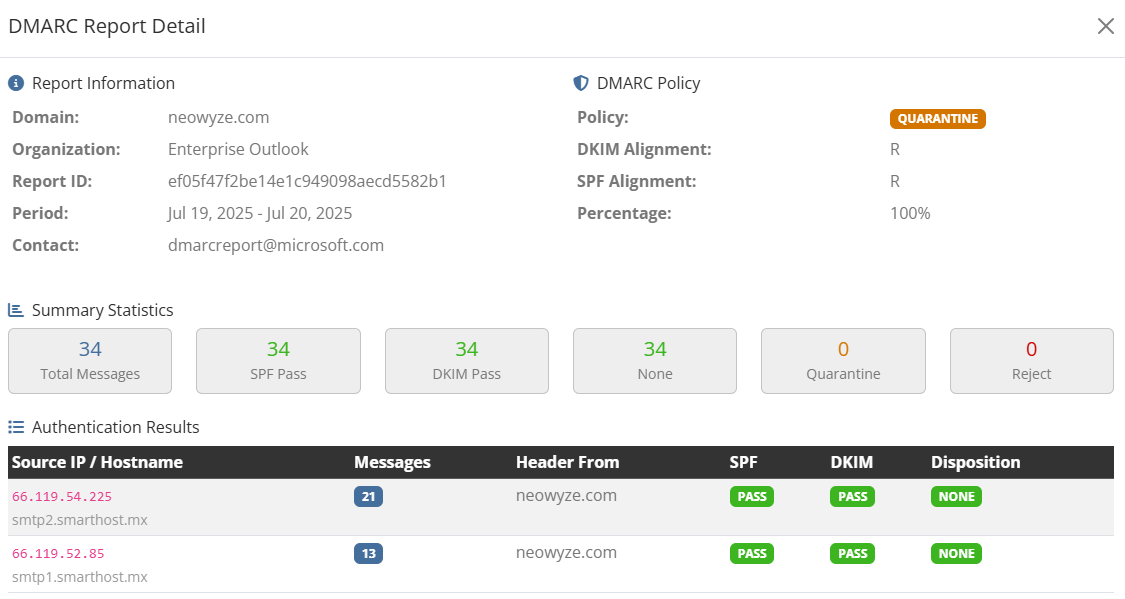
Example of DMARC report data showing authentication results and source analysis
Key Columns Explained:
| Source IP/Hostname: | Server IP and Name (if available) that sent the email |
| Messages Count: | Number of emails from this source |
| Header From: | Source Domain from message header |
| SPF Result: | Pass/Fail for SPF authentication |
| DKIM Result: | Pass/Fail for DKIM signature |
| Disposition: | Action taken (none/quarantine/reject) |